Rasa Zhukauskas MD, lead author
Principal Scientist, R&D
Axogen Corporation, Alachua, FL
The micro-CT imaging for this study was performed using SkyScan 1272 CMOS edition scanning system at Micro Photonics using previously developed system settings for all samples. Seth Hogg, PhD, Lab Manager for Micro Photonics in Allentown, PA, performed the scans.

Article Summary
Assessing the zone of injury after traumatic lacerations is incredibly challenging but getting it wrong can have significant impact on nerve repair outcomes. This study used cadaveric specimens to simulate common lacerations using a knife, broken glass, or table saw in flexor tendon zones II or V. The length of nerve damage was visually estimated under loupe magnification by expert nerve surgeons and then compared to micro-computed tomography measurements. Radiographic imaging showed fascicular damage extending beyond the surgeon’s visual assessment of epineural damage, indicating that the internal damage to nerves from traumatic lacerations was underappreciated by surgeons.
Methods
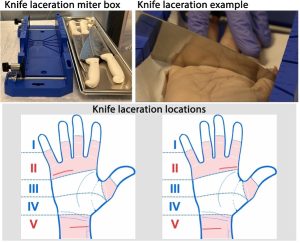
Twelve human upper extremity cadaveric specimens were used to simulate common injuries using a knife, broken glass, or table saw in flexor tendon zones II or V. The distance of nerve damage measured from the transected end was visually estimated by experienced peripheral nerve surgeons under loupe magnification. The length of nerve damage was measured radiographically using micro-computed tomography and then compared with visually estimated damage.
Results
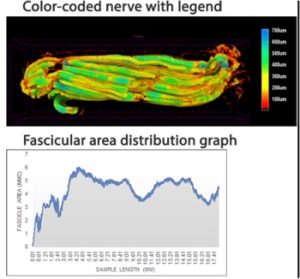
Radiographic image analysis revealed fascicular disruption extending proximally and distally from the transection, which was underestimated by visual assessment 9.5 mm on average in knife injuries, 7.8 mm in broken glass injuries, and 12.1 mm in table saw injuries. The extent of radiographic damage was similar in proximal and distal nerves, and in knife and broken glass lacerations, but most extensive in table saw lacerations.
Conclusions
Nerve damage was greatest in table saw lacerations. Radiographic imaging showed fascicular damage extending beyond the surgeon’s visual assessment of epineural damage, indicating that the internal damage to nerves from traumatic lacerations was underappreciated by surgeons. The impact this underestimated damage has on regenerative potential of an injured nerve requires further investigation.
Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2025.100833
